Naproxen-induced thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 33100559
- PMCID: PMC7549988
- DOI: 10.1080/08998280.2020.1798724
Naproxen-induced thrombocytopenia
Abstract
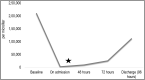
Thrombocytopenia has many mechanisms with broad differentials. A detailed history and physical, with timely diagnostic testing, is necessary to parse out the underlying etiology. Clinicians should maintain a high suspicion for drug-induced thrombocytopenia when there is an acute drop in the platelet level after exposure to commonly implicated drugs. Drug-induced thrombocytopenia is not well defined, as reporting is voluntary and not critically reviewed. Oftentimes, the culprit is not the drug itself, but a drug metabolite, which is difficult to prove with drug-dependent antibody testing. Here we present a case where naproxen led to hemarthrosis secondary to drug-induced thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: Drug-induced thrombocytopenia; hematology; internal medicine.
Copyright © 2020 Baylor University Medical Center.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Critical issues in hematology: anemia, thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, and blood product transfusions in critically ill patients.Clin Chest Med. 2003 Dec;24(4):607-22. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(03)00100-x. Clin Chest Med. 2003. PMID: 14710693 Review.
-
Drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia: incidence, clinical features, laboratory testing, and pathogenic mechanisms.Immunohematology. 2014;30(2):55-65. Immunohematology. 2014. PMID: 25247620 Review.
-
A Case of Confirmed Ceftriaxone-induced Immune Thrombocytopenia.Cureus. 2019 May 17;11(5):e4688. doi: 10.7759/cureus.4688. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31338265 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-induced and drug-dependent immune thrombocytopenias.Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2001 Sep;5(3):166-200; discussion 311-2. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-0734.2001.00041.x. Rev Clin Exp Hematol. 2001. PMID: 11703814 Review.
-
An update on evidence based diagnostic and confirmatory testing strategies for heparin induced thrombocytopenia using combined immunological and functional assays.Transfus Apher Sci. 2018 Dec;57(6):804-811. doi: 10.1016/j.transci.2018.10.019. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Transfus Apher Sci. 2018. PMID: 30401517 Review.
References
-
- Arnold D, Cuker A.. Approach to the adult with unexplained thrombocytopenia. In: Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate Inc. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-adult-with-unexplained.... Accessed May 24, 2020.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources